Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-27 Origin: Site








Choosing the right generator is a critical decision. Natural gas and diesel have key differences that affect cost, efficiency, and reliability. In this article, we compare their pros and cons so you can understand which generator suits your needs best.
Natural gas generators convert chemical energy from natural gas into electrical power. They typically connect directly to pipeline systems, allowing for a steady fuel supply without the need for storage. Many natural gas generators support both continuous and backup power applications, making them suitable for residential and industrial use. Their operation relies on controlled combustion, which drives the engine to rotate the alternator, producing electricity efficiently.
Natural gas generators produce cleaner combustion than diesel, emitting lower levels of sulfur, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This reduces the environmental impact and helps facilities meet stringent emissions regulations. They also offer cost-effective long-term operation since natural gas is often less expensive than diesel and avoids the volatility of fuel markets. Quiet operation and minimal odor make these generators ideal for urban settings or noise-sensitive locations. Additionally, the fuel's pipeline availability eliminates storage concerns and simplifies logistics.
Despite their advantages, natural gas generators have limitations. They rely heavily on pipeline supply, which can be disrupted during storms or natural disasters, leading to potential downtime. Natural gas is highly flammable, posing safety risks if leaks occur. Additionally, in certain scenarios, natural gas generators can emit more carbon dioxide per unit of energy compared to diesel, slightly reducing their overall environmental advantage. Initial installation costs may also be higher due to pipeline integration requirements.
Natural gas generators excel in urban areas with established pipeline infrastructure. They are well-suited for long-term, continuous power needs in offices, hospitals, and manufacturing facilities. Locations that prioritize environmental sustainability benefit from their cleaner combustion and lower operational emissions. These generators are also preferable where space for fuel storage is limited, as they eliminate the need for on-site fuel tanks.
Diesel generators consist of a diesel engine and an alternator. They operate independently of pipelines, storing fuel on-site, which ensures availability in remote or off-grid locations. The diesel engine combusts fuel to drive the alternator, producing electricity for high-demand or emergency applications. Diesel generators are versatile, supporting both intermittent and continuous power, depending on the installed capacity and usage scenario.
Diesel generators offer high energy density, delivering significant output per unit of fuel. They are reliable for emergency backup and critical operations, such as hospitals and industrial plants. Diesel engines are durable, with long lifespans exceeding 20 years under proper maintenance. They do not require spark plugs, which reduces maintenance complexity and enhances operational safety. Diesel fuel is also less flammable than natural gas, mitigating certain fire risks.
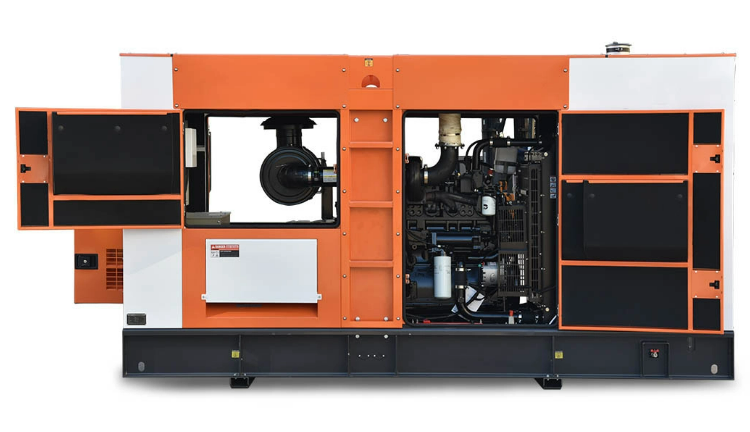
Despite durability, diesel generators have higher upfront costs compared to natural gas units. Noise pollution can be significant, especially for older models, which may affect nearby residents or office environments. Diesel generators are also bulky, reducing portability and complicating installation in limited spaces. Environmental concerns are notable, as diesel combustion produces higher emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, potentially triggering compliance challenges.
Diesel generators are optimal for high-load, intermittent, or off-grid applications. They suit construction sites, agricultural operations, hospitals, and industrial plants where continuous and reliable power is critical. In locations lacking natural gas pipelines, diesel offers a self-contained energy solution with immediate availability. Additionally, they are appropriate for facilities with on-site fuel storage capabilities that prioritize backup readiness.
Diesel generators generally provide higher fuel efficiency per unit of energy, while natural gas units tend to be more cost-effective in regions with low gas prices. Comparing diesel vs natural gas generator maintenance costs reveals that diesel units often require more frequent servicing due to fuel impurities, while natural gas units need attention to spark plugs and pipeline connections. Over time, fuel costs and operational efficiency significantly influence total expenditure.
Feature | Natural Gas Generator | Diesel Generator |
Fuel Efficiency | Moderate | High |
Fuel Cost | Lower in urban areas | Higher, volatile |
Maintenance | Spark plug replacement, pipeline checks | Regular engine maintenance, fuel system cleaning |
Environmental Impact | Lower NOx, SOx | Higher emissions, CO₂ comparable |
Noise Level | Quieter | Louder |
Natural gas generators emit fewer pollutants than diesel, producing cleaner air in urban and industrial settings. However, they may release higher CO₂ under certain conditions. Diesel generators are known for higher nitrogen oxide and particulate emissions, increasing environmental compliance requirements. Noise and odor differences are notable, as natural gas generators operate quietly with minimal smell, whereas diesel units may generate noticeable sound and fumes.
Diesel generators are highly reliable, with fuel stored on-site ensuring uninterrupted operation during emergencies. Natural gas generators depend on continuous pipeline access, making them more susceptible to supply interruptions. Maintenance for diesel engines is routine but essential for longevity, while natural gas units require less intensive upkeep. Understanding diesel vs natural gas generator maintenance costs is critical for budgeting operational expenditures.
Safety varies between fuel types. Diesel is less flammable and safer for on-site storage, whereas natural gas is highly combustible, requiring leak detection and ventilation precautions. Proper safety protocols, including fire suppression and pipeline monitoring, are essential. Both fuel types carry operational risks if mismanaged, highlighting the need for thorough staff training and adherence to installation guidelines.
Natural gas generators are lighter and often easier to install in urban environments, provided pipeline access exists. Diesel generators require larger physical space due to fuel storage needs and engine bulkiness. Relocation is simpler for natural gas units if needed, while diesel may involve significant logistical planning. Installation complexity affects both upfront costs and long-term operational flexibility.
Both generator types can operate for 20-25 years under proper maintenance. Diesel engines are sturdy and excel under high-load or intermittent operation. Natural gas generators perform reliably in continuous low-load conditions and are less prone to certain engine wear issues. Performance under varying operational demands informs the long-term value of the generator investment.
Diesel generators generally require higher initial investment due to engine complexity and on-site fuel infrastructure. Natural gas generators may incur pipeline connection costs but tend to have lower equipment pricing. Installation complexity, space requirements, and site preparation influence overall expenditure. Evaluating total upfront costs ensures the selected generator aligns with both financial and operational constraints.

Fuel costs impact long-term operational budgets. Natural gas prices are often more stable in urban areas with established pipelines, while diesel costs fluctuate with global oil markets. Comparing diesel generator fuel consumption and natural gas costs highlights the importance of evaluating local pricing trends. Energy procurement strategies can optimize fuel expenses for long-term savings.
Routine maintenance differs for each generator type. Diesel engines require regular checks of filters, injectors, and oil systems. Natural gas units need spark plug replacement and occasional pipeline inspection. Over time, diesel units may incur higher repair costs due to mechanical complexity, whereas natural gas generators benefit from simpler engine design. Factoring diesel vs natural gas generator maintenance costs informs accurate budgeting.
Return on investment depends on balancing upfront cost, fuel efficiency, and maintenance expenses. While diesel generators may offer high energy density and reliability, natural gas generators can reduce operational costs and environmental liabilities. Decision-making should consider both immediate financial constraints and long-term value derived from efficiency, emissions, and safety performance.
Diesel generators face stringent regulations, including EPA Tier 4 and BACT requirements. Compliance necessitates investment in emission control technologies, such as filters and scrubbers. Natural gas generators typically face less regulatory burden due to cleaner combustion, simplifying operational oversight. Understanding current and future regulations ensures uninterrupted compliance and avoids penalties.
Natural gas generators contribute to lower emissions, aligning with corporate sustainability goals. They provide regulatory flexibility, reduce pollution, and may qualify for incentives promoting cleaner energy use. This can influence long-term operational planning, particularly in environmentally conscious industries.
Both generator types require proper permitting, inspection, and adherence to local safety codes. Installation must comply with building, electrical, and fire safety standards. While natural gas pipelines require additional safety monitoring, diesel units necessitate safe storage and spill containment plans. Ensuring regulatory compliance minimizes operational risk.
Technological advancements aim to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Cleaner diesel alternatives and biodiesel blends are emerging, while natural gas generator designs continue to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce maintenance needs. Staying informed on trends allows businesses to invest in generators that remain competitive and compliant in the future.
Evaluate peak load, continuous vs intermittent usage, and critical systems to determine the appropriate generator size. High-demand facilities may favor diesel generators, while long-term, steady loads may benefit from natural gas units. Accurate assessment ensures reliable performance without oversizing or underutilization.
Access to natural gas pipelines or on-site diesel storage is a key factor. Limited pipeline availability necessitates diesel generators, whereas continuous gas supply can make natural gas units more convenient. Fuel accessibility directly impacts operational continuity during emergencies.
Upfront costs and operational efficiency must be weighed. Diesel units require higher initial investment but may deliver higher energy density. Natural gas units can reduce long-term fuel costs and maintenance expenses. Aligning budget with expected operational needs ensures the most cost-effective solution.
Natural gas generators support sustainability initiatives due to lower emissions and cleaner combustion. Diesel units may require emission control technologies to meet environmental standards. Organizations with corporate responsibility targets should consider fuel type impact on long-term compliance and ESG reporting.
Fire hazards, fuel supply disruptions, and flammability risks must be evaluated. Diesel generators store fuel safely on-site, while natural gas units rely on pipelines, which can be interrupted. Incorporating preventive measures and monitoring systems reduces operational risk.
Choosing the right generator requires weighing multiple factors: efficiency, reliability, maintenance, fuel costs, environmental impact, and installation requirements. Step-by-step evaluation helps ensure the selected generator aligns with operational goals. Consulting experts can optimize generator selection for specific applications and local conditions.
Both natural gas and diesel generators have clear pros and cons. Diesel units deliver high energy, reliability, and suit heavy-load sites. Natural gas units run cleaner, quieter, and reduce long-term fuel costs. ZHEJIANG UNIVERSAL MACHINERY CO., LTD. offers generators that combine durability and efficiency, providing reliable power solutions and excellent value for businesses.
A: Diesel generators offer high energy density and reliability, while natural gas generators run cleaner and quieter. Comparing natural gas vs diesel generator efficiency helps determine the best fit for your needs.
A: Natural gas generators often lower operational costs due to cheaper fuel and reduced maintenance. Consider diesel vs natural gas generator maintenance costs when budgeting.
A: Natural gas generators emit fewer pollutants, while diesel produces higher NOx and particulate matter. Evaluating natural gas generator emissions vs diesel supports environmental decisions.
A: Diesel generators store fuel on-site, making them ideal for off-grid sites. Diesel generator fuel consumption comparison is crucial for planning fuel supply efficiently.
A: Diesel engines need routine servicing, while natural gas generators require spark plug checks and pipeline inspection. Diesel vs natural gas generator maintenance costs should guide upkeep schedules.